Nota
Haga clic aquí para descargar el código de ejemplo completo
Múltiples ejes Y con espinas #
Cree múltiples ejes y con un eje x compartido. Esto se hace creando twinxejes, volviendo invisibles todos los lomos excepto el derecho y compensando su posición usando set_position.
Tenga en cuenta que este enfoque utiliza matplotlib.axes.Axesy sus
Spines. En los ejemplos de demostración de Parasite Axes y
Parasite Axes se muestra un enfoque alternativo para los ejes parásitos .
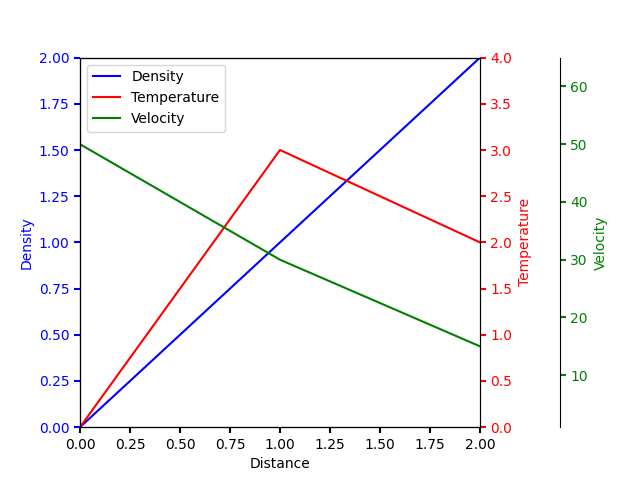
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
fig.subplots_adjust(right=0.75)
twin1 = ax.twinx()
twin2 = ax.twinx()
# Offset the right spine of twin2. The ticks and label have already been
# placed on the right by twinx above.
twin2.spines.right.set_position(("axes", 1.2))
p1, = ax.plot([0, 1, 2], [0, 1, 2], "b-", label="Density")
p2, = twin1.plot([0, 1, 2], [0, 3, 2], "r-", label="Temperature")
p3, = twin2.plot([0, 1, 2], [50, 30, 15], "g-", label="Velocity")
ax.set_xlim(0, 2)
ax.set_ylim(0, 2)
twin1.set_ylim(0, 4)
twin2.set_ylim(1, 65)
ax.set_xlabel("Distance")
ax.set_ylabel("Density")
twin1.set_ylabel("Temperature")
twin2.set_ylabel("Velocity")
ax.yaxis.label.set_color(p1.get_color())
twin1.yaxis.label.set_color(p2.get_color())
twin2.yaxis.label.set_color(p3.get_color())
tkw = dict(size=4, width=1.5)
ax.tick_params(axis='y', colors=p1.get_color(), **tkw)
twin1.tick_params(axis='y', colors=p2.get_color(), **tkw)
twin2.tick_params(axis='y', colors=p3.get_color(), **tkw)
ax.tick_params(axis='x', **tkw)
ax.legend(handles=[p1, p2, p3])
plt.show()