Nota
Haga clic aquí para descargar el código de ejemplo completo
Anotar Transformar #
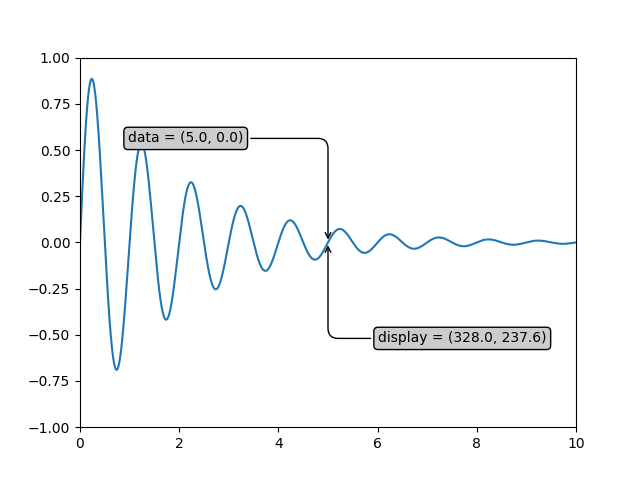
Este ejemplo muestra cómo usar diferentes sistemas de coordenadas para las anotaciones. Para obtener una descripción general completa de las capacidades de anotación, consulte también el tutorial de anotación .
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.arange(0, 10, 0.005)
y = np.exp(-x/2.) * np.sin(2*np.pi*x)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_xlim(0, 10)
ax.set_ylim(-1, 1)
xdata, ydata = 5, 0
xdisplay, ydisplay = ax.transData.transform((xdata, ydata))
bbox = dict(boxstyle="round", fc="0.8")
arrowprops = dict(
arrowstyle="->",
connectionstyle="angle,angleA=0,angleB=90,rad=10")
offset = 72
ax.annotate(
f'data = ({xdata:.1f}, {ydata:.1f})',
(xdata, ydata),
xytext=(-2*offset, offset), textcoords='offset points',
bbox=bbox, arrowprops=arrowprops)
ax.annotate(
f'display = ({xdisplay:.1f}, {ydisplay:.1f})',
xy=(xdisplay, ydisplay), xycoords='figure pixels',
xytext=(0.5*offset, -offset), textcoords='offset points',
bbox=bbox, arrowprops=arrowprops)
plt.show()
Referencias
En este ejemplo se muestra el uso de las siguientes funciones, métodos, clases y módulos: