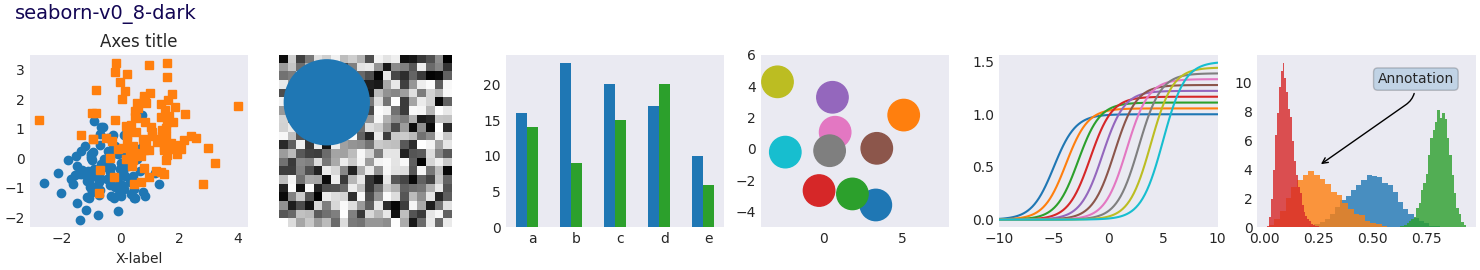
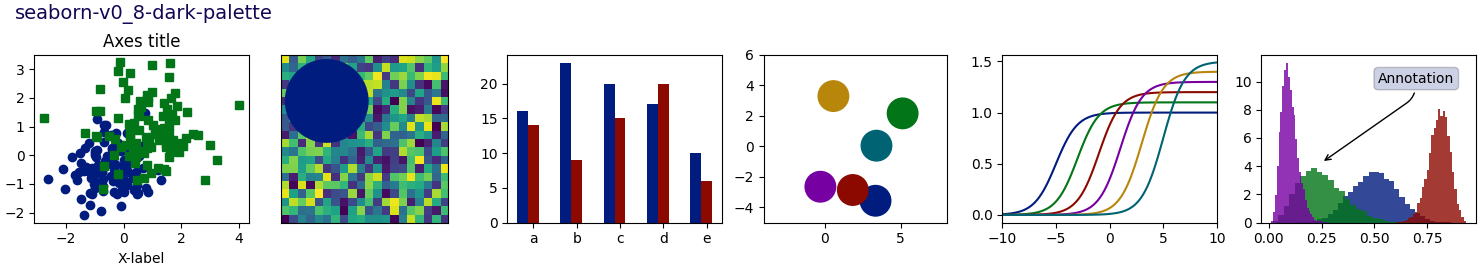
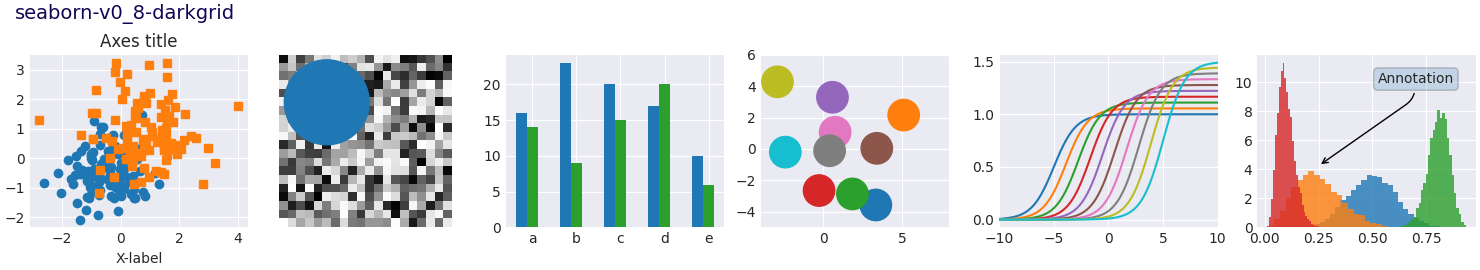
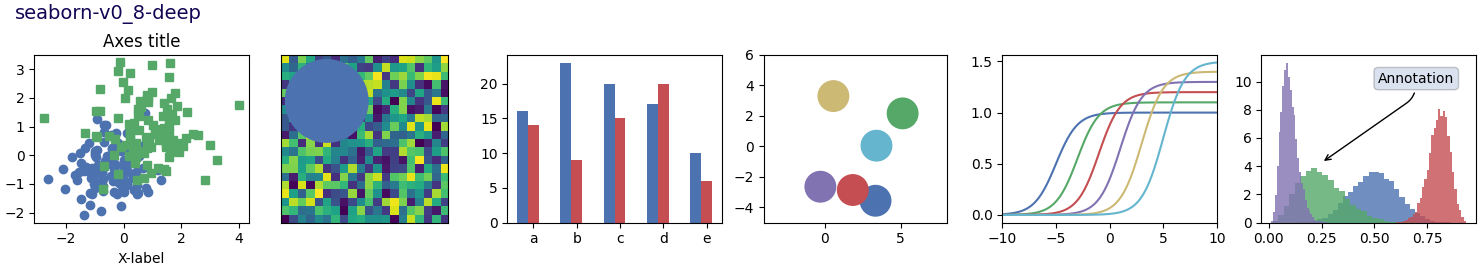
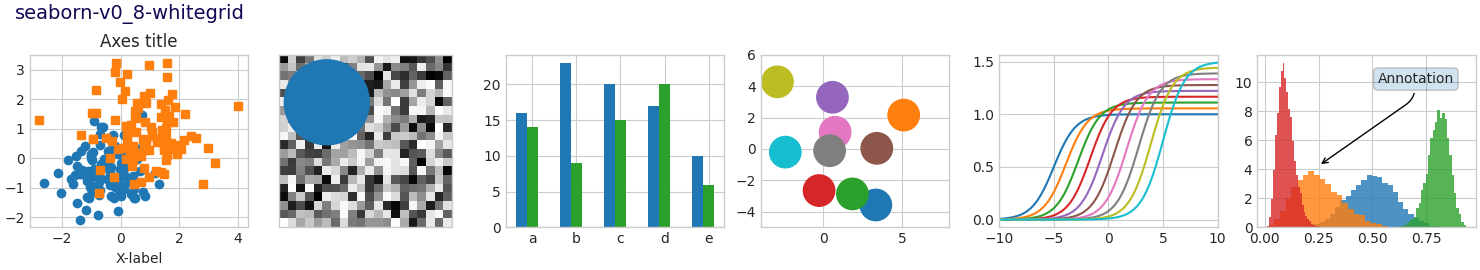
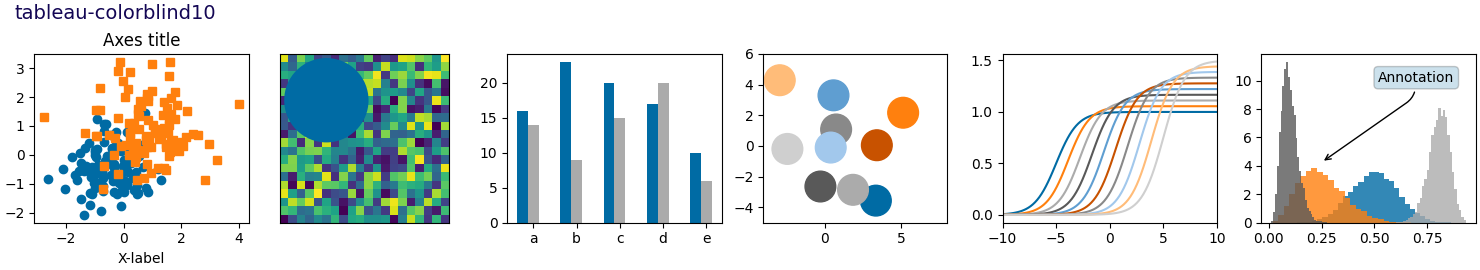
Nota
Haga clic aquí para descargar el código de ejemplo completo
Número de referencia de las hojas de estilo
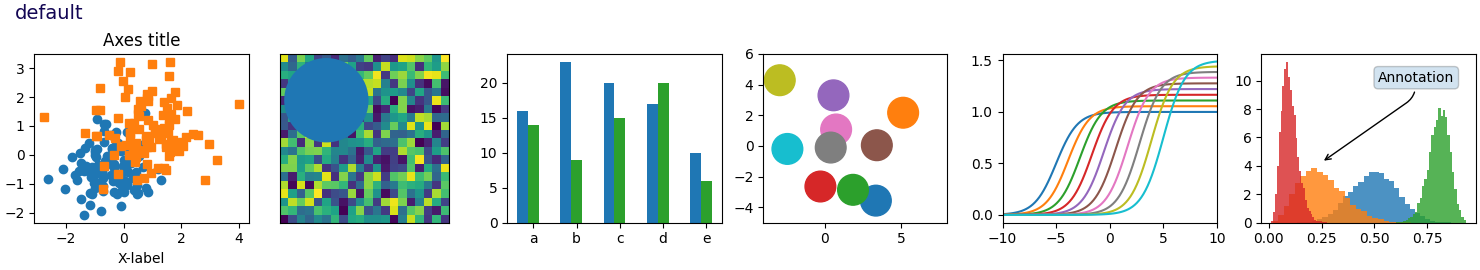
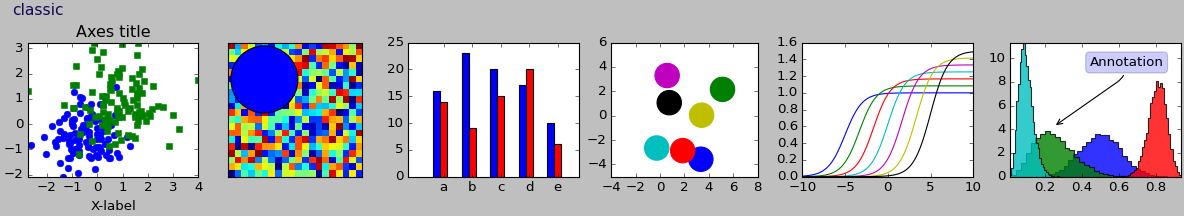
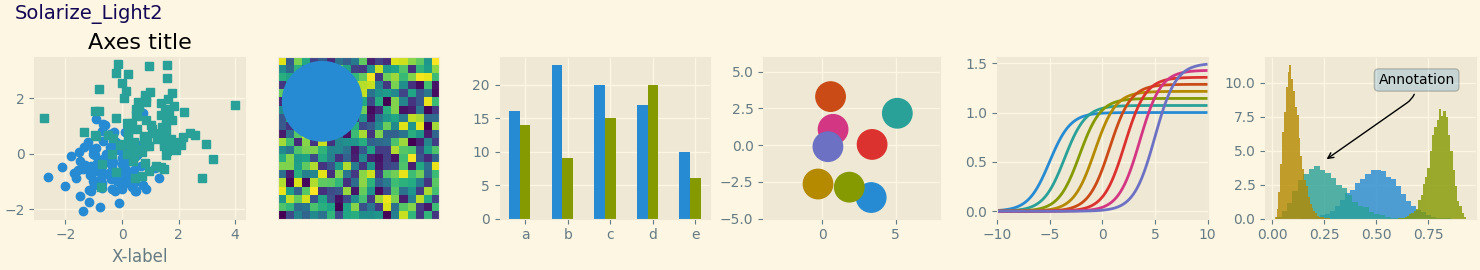
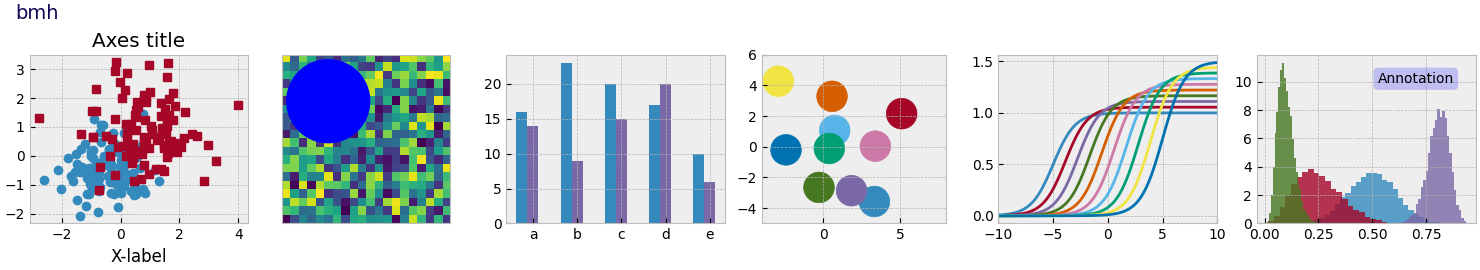
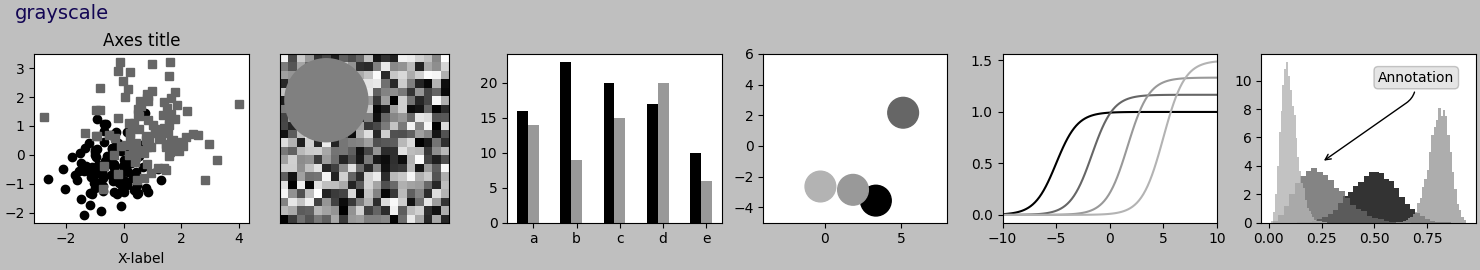
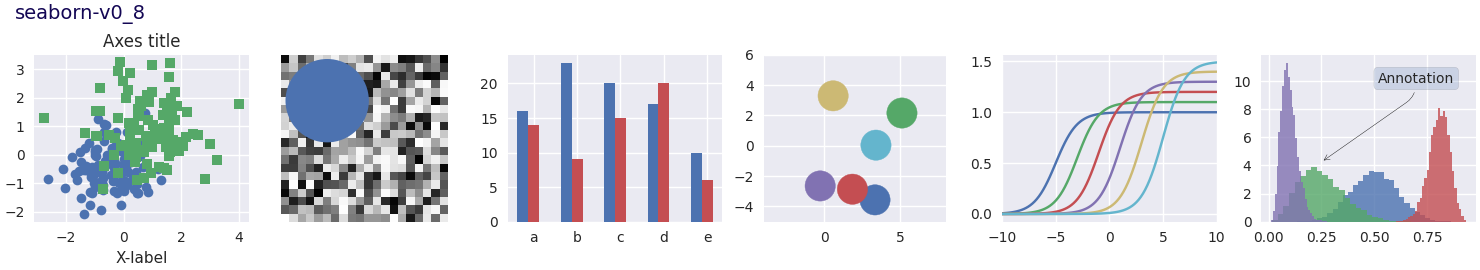
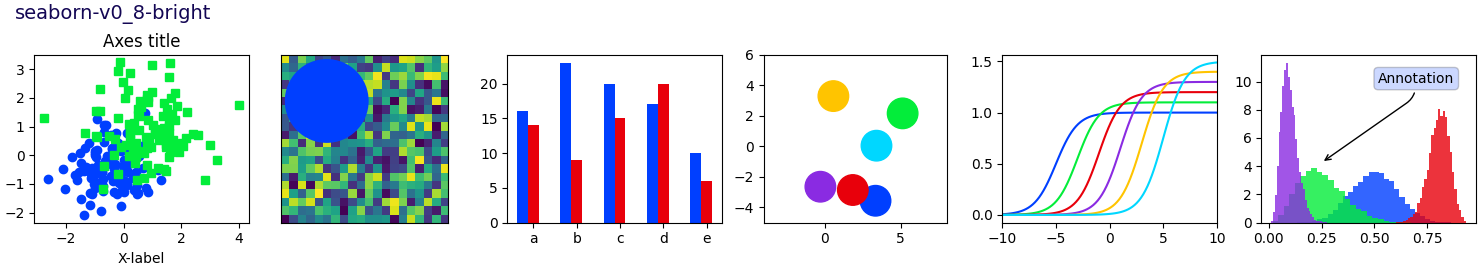
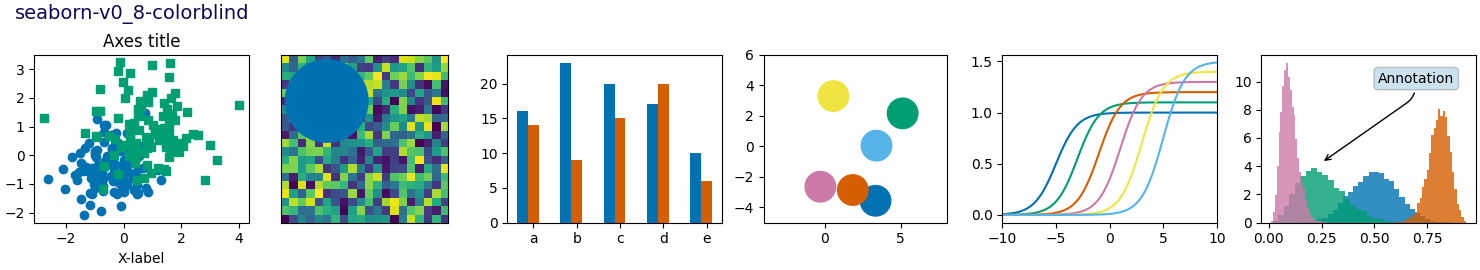
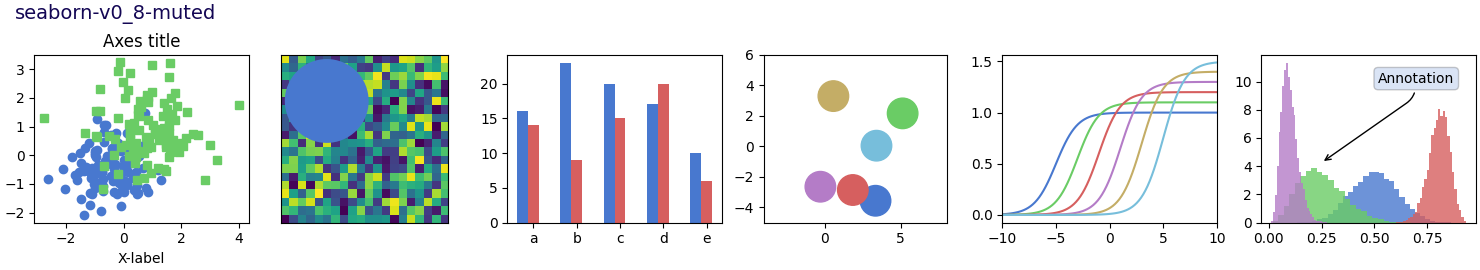
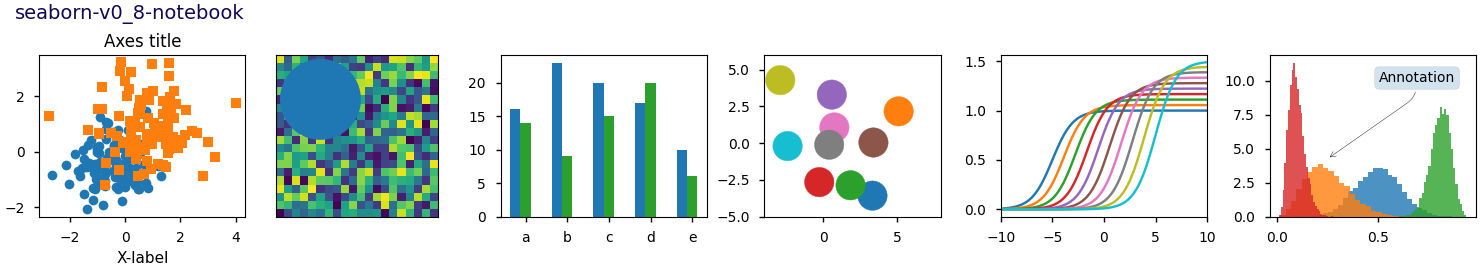
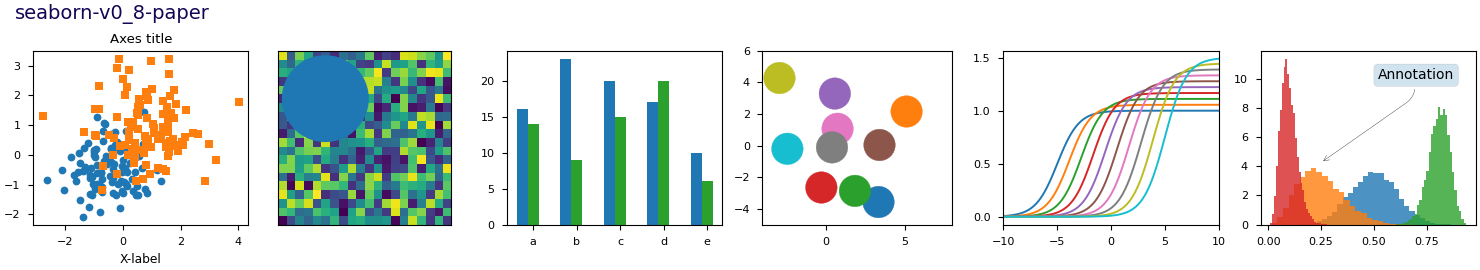
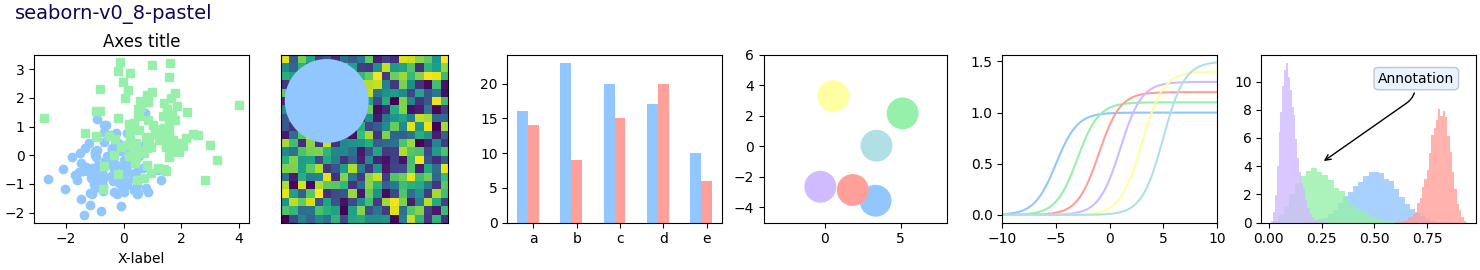
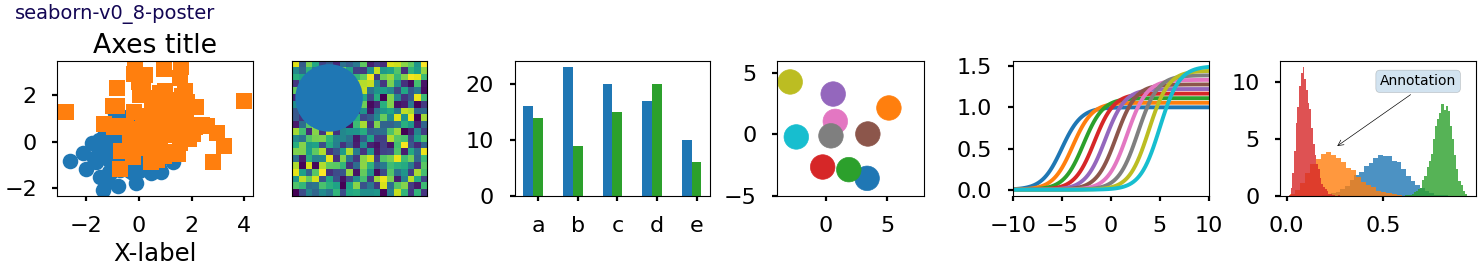
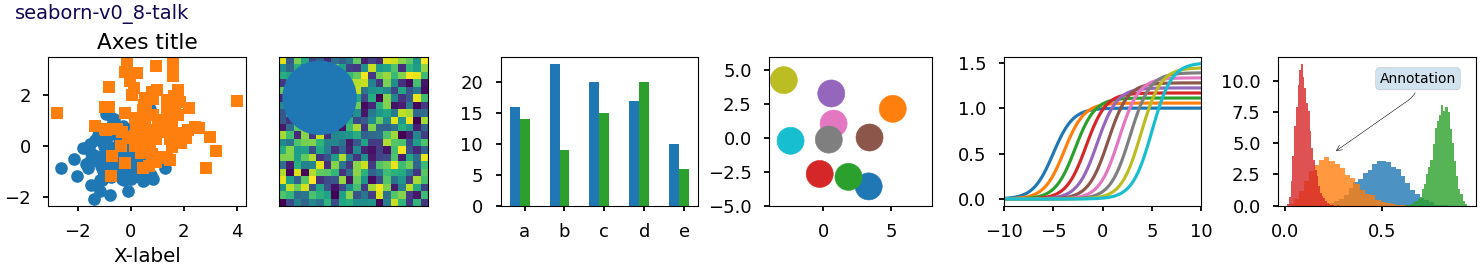
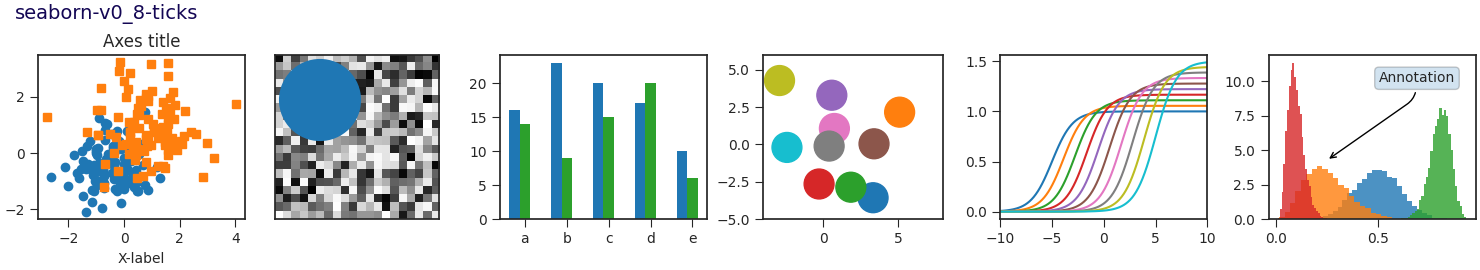
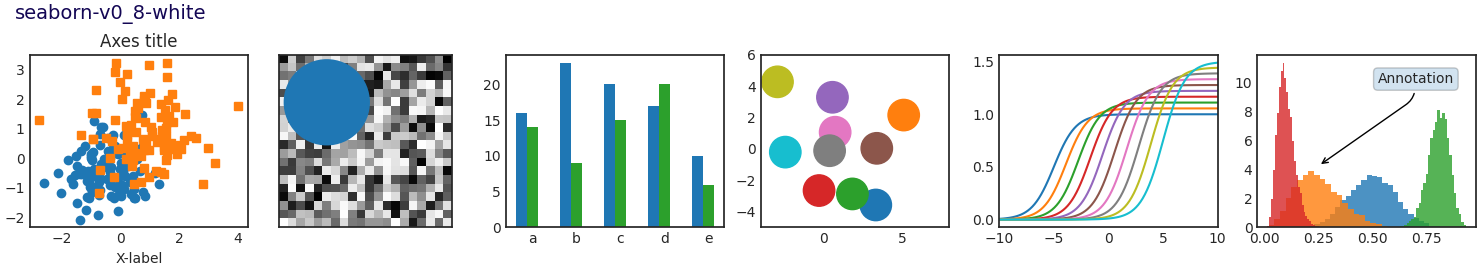
Este script demuestra las diferentes hojas de estilo disponibles en un conjunto común de gráficos de ejemplo: gráfico de dispersión, imagen, gráfico de barras, parches, gráfico de líneas e histograma.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.colors as mcolors
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
def plot_scatter(ax, prng, nb_samples=100):
"""Scatter plot."""
for mu, sigma, marker in [(-.5, 0.75, 'o'), (0.75, 1., 's')]:
x, y = prng.normal(loc=mu, scale=sigma, size=(2, nb_samples))
ax.plot(x, y, ls='none', marker=marker)
ax.set_xlabel('X-label')
ax.set_title('Axes title')
return ax
def plot_colored_lines(ax):
"""Plot lines with colors following the style color cycle."""
t = np.linspace(-10, 10, 100)
def sigmoid(t, t0):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-(t - t0)))
nb_colors = len(plt.rcParams['axes.prop_cycle'])
shifts = np.linspace(-5, 5, nb_colors)
amplitudes = np.linspace(1, 1.5, nb_colors)
for t0, a in zip(shifts, amplitudes):
ax.plot(t, a * sigmoid(t, t0), '-')
ax.set_xlim(-10, 10)
return ax
def plot_bar_graphs(ax, prng, min_value=5, max_value=25, nb_samples=5):
"""Plot two bar graphs side by side, with letters as x-tick labels."""
x = np.arange(nb_samples)
ya, yb = prng.randint(min_value, max_value, size=(2, nb_samples))
width = 0.25
ax.bar(x, ya, width)
ax.bar(x + width, yb, width, color='C2')
ax.set_xticks(x + width, labels=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'])
return ax
def plot_colored_circles(ax, prng, nb_samples=15):
"""
Plot circle patches.
NB: draws a fixed amount of samples, rather than using the length of
the color cycle, because different styles may have different numbers
of colors.
"""
for sty_dict, j in zip(plt.rcParams['axes.prop_cycle'], range(nb_samples)):
ax.add_patch(plt.Circle(prng.normal(scale=3, size=2),
radius=1.0, color=sty_dict['color']))
# Force the limits to be the same across the styles (because different
# styles may have different numbers of available colors).
ax.set_xlim([-4, 8])
ax.set_ylim([-5, 6])
ax.set_aspect('equal', adjustable='box') # to plot circles as circles
return ax
def plot_image_and_patch(ax, prng, size=(20, 20)):
"""Plot an image with random values and superimpose a circular patch."""
values = prng.random_sample(size=size)
ax.imshow(values, interpolation='none')
c = plt.Circle((5, 5), radius=5, label='patch')
ax.add_patch(c)
# Remove ticks
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
def plot_histograms(ax, prng, nb_samples=10000):
"""Plot 4 histograms and a text annotation."""
params = ((10, 10), (4, 12), (50, 12), (6, 55))
for a, b in params:
values = prng.beta(a, b, size=nb_samples)
ax.hist(values, histtype="stepfilled", bins=30,
alpha=0.8, density=True)
# Add a small annotation.
ax.annotate('Annotation', xy=(0.25, 4.25),
xytext=(0.9, 0.9), textcoords=ax.transAxes,
va="top", ha="right",
bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", alpha=0.2),
arrowprops=dict(
arrowstyle="->",
connectionstyle="angle,angleA=-95,angleB=35,rad=10"),
)
return ax
def plot_figure(style_label=""):
"""Setup and plot the demonstration figure with a given style."""
# Use a dedicated RandomState instance to draw the same "random" values
# across the different figures.
prng = np.random.RandomState(96917002)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(ncols=6, nrows=1, num=style_label,
figsize=(14.8, 2.7), constrained_layout=True)
# make a suptitle, in the same style for all subfigures,
# except those with dark backgrounds, which get a lighter color:
background_color = mcolors.rgb_to_hsv(
mcolors.to_rgb(plt.rcParams['figure.facecolor']))[2]
if background_color < 0.5:
title_color = [0.8, 0.8, 1]
else:
title_color = np.array([19, 6, 84]) / 256
fig.suptitle(style_label, x=0.01, ha='left', color=title_color,
fontsize=14, fontfamily='DejaVu Sans', fontweight='normal')
plot_scatter(axs[0], prng)
plot_image_and_patch(axs[1], prng)
plot_bar_graphs(axs[2], prng)
plot_colored_circles(axs[3], prng)
plot_colored_lines(axs[4])
plot_histograms(axs[5], prng)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Setup a list of all available styles, in alphabetical order but
# the `default` and `classic` ones, which will be forced resp. in
# first and second position.
# styles with leading underscores are for internal use such as testing
# and plot types gallery. These are excluded here.
style_list = ['default', 'classic'] + sorted(
style for style in plt.style.available
if style != 'classic' and not style.startswith('_'))
# Plot a demonstration figure for every available style sheet.
for style_label in style_list:
with plt.rc_context({"figure.max_open_warning": len(style_list)}):
with plt.style.context(style_label):
plot_figure(style_label=style_label)
plt.show()
Tiempo total de ejecución del script: (0 minutos 29,495 segundos)