Nota
Haga clic aquí para descargar el código de ejemplo completo
Deslizador #
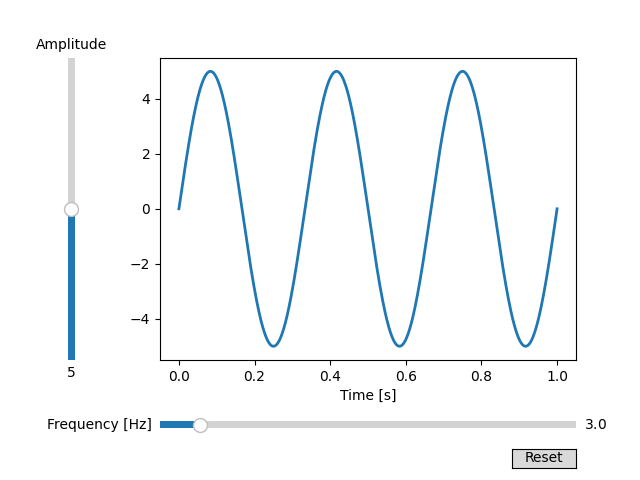
En este ejemplo, los controles deslizantes se utilizan para controlar la frecuencia y la amplitud de una onda sinusoidal.
Consulte Ajuste de controles deslizantes a valores discretos para ver un ejemplo de Sliderajuste a valores discretos.
Consulte Umbral de una imagen con RangeSlider para ver un ejemplo del uso de a RangeSliderpara definir un rango de valores.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Slider, Button
# The parametrized function to be plotted
def f(t, amplitude, frequency):
return amplitude * np.sin(2 * np.pi * frequency * t)
t = np.linspace(0, 1, 1000)
# Define initial parameters
init_amplitude = 5
init_frequency = 3
# Create the figure and the line that we will manipulate
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
line, = ax.plot(t, f(t, init_amplitude, init_frequency), lw=2)
ax.set_xlabel('Time [s]')
# adjust the main plot to make room for the sliders
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.25, bottom=0.25)
# Make a horizontal slider to control the frequency.
axfreq = fig.add_axes([0.25, 0.1, 0.65, 0.03])
freq_slider = Slider(
ax=axfreq,
label='Frequency [Hz]',
valmin=0.1,
valmax=30,
valinit=init_frequency,
)
# Make a vertically oriented slider to control the amplitude
axamp = fig.add_axes([0.1, 0.25, 0.0225, 0.63])
amp_slider = Slider(
ax=axamp,
label="Amplitude",
valmin=0,
valmax=10,
valinit=init_amplitude,
orientation="vertical"
)
# The function to be called anytime a slider's value changes
def update(val):
line.set_ydata(f(t, amp_slider.val, freq_slider.val))
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
# register the update function with each slider
freq_slider.on_changed(update)
amp_slider.on_changed(update)
# Create a `matplotlib.widgets.Button` to reset the sliders to initial values.
resetax = fig.add_axes([0.8, 0.025, 0.1, 0.04])
button = Button(resetax, 'Reset', hovercolor='0.975')
def reset(event):
freq_slider.reset()
amp_slider.reset()
button.on_clicked(reset)
plt.show()
Referencias
En este ejemplo se muestra el uso de las siguientes funciones, métodos, clases y módulos: