Nota
Haga clic aquí para descargar el código de ejemplo completo
Líneas multicolores #
Este ejemplo muestra cómo hacer una línea multicolor. En este ejemplo, la línea está coloreada según su derivada.
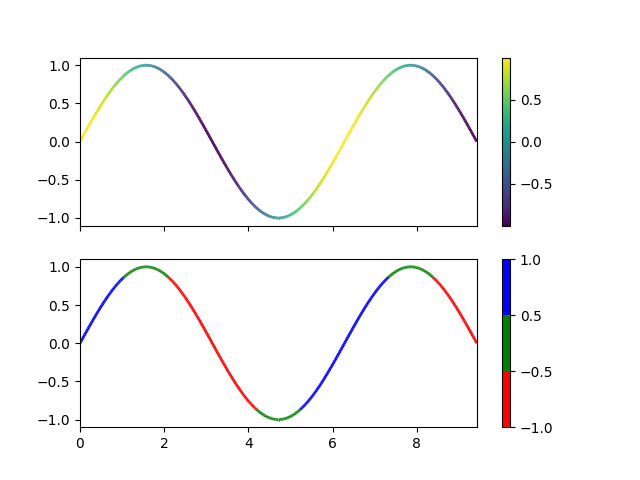
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.collections import LineCollection
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap, BoundaryNorm
x = np.linspace(0, 3 * np.pi, 500)
y = np.sin(x)
dydx = np.cos(0.5 * (x[:-1] + x[1:])) # first derivative
# Create a set of line segments so that we can color them individually
# This creates the points as a N x 1 x 2 array so that we can stack points
# together easily to get the segments. The segments array for line collection
# needs to be (numlines) x (points per line) x 2 (for x and y)
points = np.array([x, y]).T.reshape(-1, 1, 2)
segments = np.concatenate([points[:-1], points[1:]], axis=1)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=True, sharey=True)
# Create a continuous norm to map from data points to colors
norm = plt.Normalize(dydx.min(), dydx.max())
lc = LineCollection(segments, cmap='viridis', norm=norm)
# Set the values used for colormapping
lc.set_array(dydx)
lc.set_linewidth(2)
line = axs[0].add_collection(lc)
fig.colorbar(line, ax=axs[0])
# Use a boundary norm instead
cmap = ListedColormap(['r', 'g', 'b'])
norm = BoundaryNorm([-1, -0.5, 0.5, 1], cmap.N)
lc = LineCollection(segments, cmap=cmap, norm=norm)
lc.set_array(dydx)
lc.set_linewidth(2)
line = axs[1].add_collection(lc)
fig.colorbar(line, ax=axs[1])
axs[0].set_xlim(x.min(), x.max())
axs[0].set_ylim(-1.1, 1.1)
plt.show()