Nota
Haga clic aquí para descargar el código de ejemplo completo
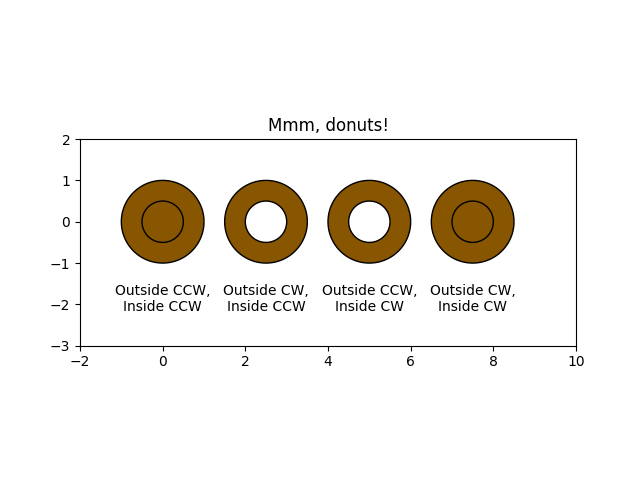
mmm donas!!! #
Dibuja donas (¡miam!) usando Paths y PathPatches. Este ejemplo muestra el efecto de las orientaciones de la ruta en una ruta compuesta.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.path as mpath
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def wise(v):
if v == 1:
return "CCW"
else:
return "CW"
def make_circle(r):
t = np.arange(0, np.pi * 2.0, 0.01)
t = t.reshape((len(t), 1))
x = r * np.cos(t)
y = r * np.sin(t)
return np.hstack((x, y))
Path = mpath.Path
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
inside_vertices = make_circle(0.5)
outside_vertices = make_circle(1.0)
codes = np.ones(
len(inside_vertices), dtype=mpath.Path.code_type) * mpath.Path.LINETO
codes[0] = mpath.Path.MOVETO
for i, (inside, outside) in enumerate(((1, 1), (1, -1), (-1, 1), (-1, -1))):
# Concatenate the inside and outside subpaths together, changing their
# order as needed
vertices = np.concatenate((outside_vertices[::outside],
inside_vertices[::inside]))
# Shift the path
vertices[:, 0] += i * 2.5
# The codes will be all "LINETO" commands, except for "MOVETO"s at the
# beginning of each subpath
all_codes = np.concatenate((codes, codes))
# Create the Path object
path = mpath.Path(vertices, all_codes)
# Add plot it
patch = mpatches.PathPatch(path, facecolor='#885500', edgecolor='black')
ax.add_patch(patch)
ax.annotate("Outside %s,\nInside %s" % (wise(outside), wise(inside)),
(i * 2.5, -1.5), va="top", ha="center")
ax.set_xlim(-2, 10)
ax.set_ylim(-3, 2)
ax.set_title('Mmm, donuts!')
ax.set_aspect(1.0)
plt.show()
Referencias
En este ejemplo se muestra el uso de las siguientes funciones, métodos, clases y módulos: