Nota
Haga clic aquí para descargar el código de ejemplo completo
HBoxDividerdemostración #
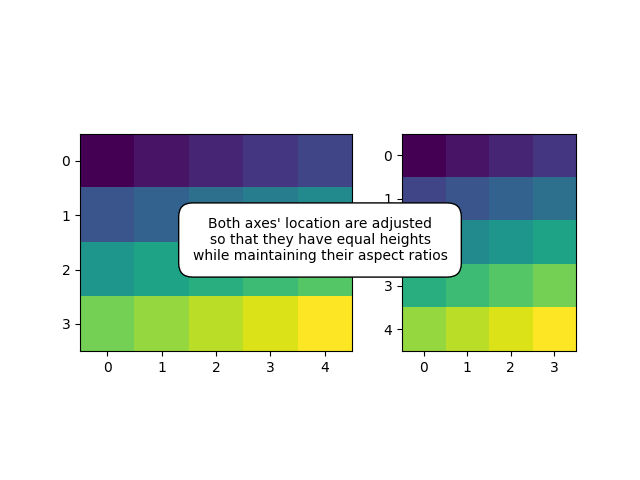
Uso de an HBoxDividerpara organizar subparcelas.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.axes_divider import HBoxDivider
import mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.axes_size as Size
def make_heights_equal(fig, rect, ax1, ax2, pad):
# pad in inches
divider = HBoxDivider(
fig, rect,
horizontal=[Size.AxesX(ax1), Size.Fixed(pad), Size.AxesX(ax2)],
vertical=[Size.AxesY(ax1), Size.Scaled(1), Size.AxesY(ax2)])
ax1.set_axes_locator(divider.new_locator(0))
ax2.set_axes_locator(divider.new_locator(2))
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr1 = np.arange(20).reshape((4, 5))
arr2 = np.arange(20).reshape((5, 4))
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
ax1.imshow(arr1)
ax2.imshow(arr2)
make_heights_equal(fig, 111, ax1, ax2, pad=0.5)
fig.text(.5, .5,
"Both axes' location are adjusted\n"
"so that they have equal heights\n"
"while maintaining their aspect ratios",
va="center", ha="center",
bbox=dict(boxstyle="round, pad=1", facecolor="w"))
plt.show()